Ningbo and Shanghai, the world’s two largest ports, experience unprecedented congestion
The world’s two largest ports are experiencing unprecedented volumes of tankers, bulk carriers and containerships back up into the East China Sea as a combination of renewed Covid cases, fierce weather and strong US demand creates further supply chain havoc.
Ningbo-Zhoushan and Shanghai to the north handled 1.17bn and 510m tons in 2020, marking them out once again as the world’s top two ports. In container terms, they’re also on the podium – Shanghai ranked number one in the world with Ningbo-Zhoushan in third place.
The two ports were hit hard by a typhoon late last month and have seen productivity slow as new anti-Covid measures are being carried out at most Chinese quaysides in the wake of the sudden spread of the delta variant of Covid-19 over the past three weeks.
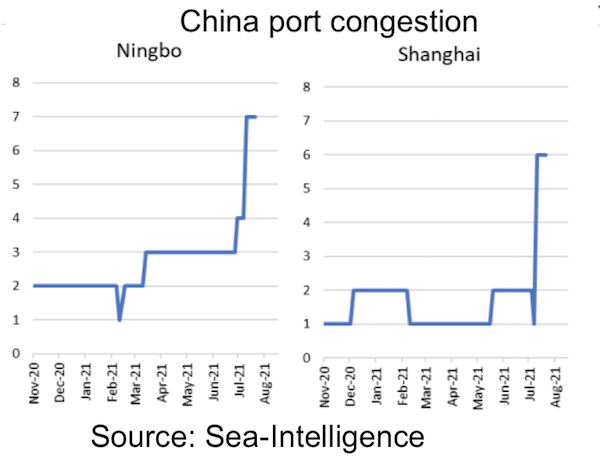
Copenhagen-based Sea-Intelligence has carried out a data-led inspection of container port congestion at 22 ports around the world. The results, published yesterday, show Shanghai and Ningbo recently coming under huge pressure from growing congestion (see inset graph).
Putting these figures in context, among the 22 ports surveyed, only Los Angeles, Long Beach, Oakland, Rotterdam, Antwerp and Vietnam had more severe congestion than China’s big two ports.
“In terms of Ningbo and Shanghai, this might be an early warning of coming impact of more Covid restrictions in China, as the delta variant appears to continue to be present,” Sea-Intelligence noted in its most recent weekly report.
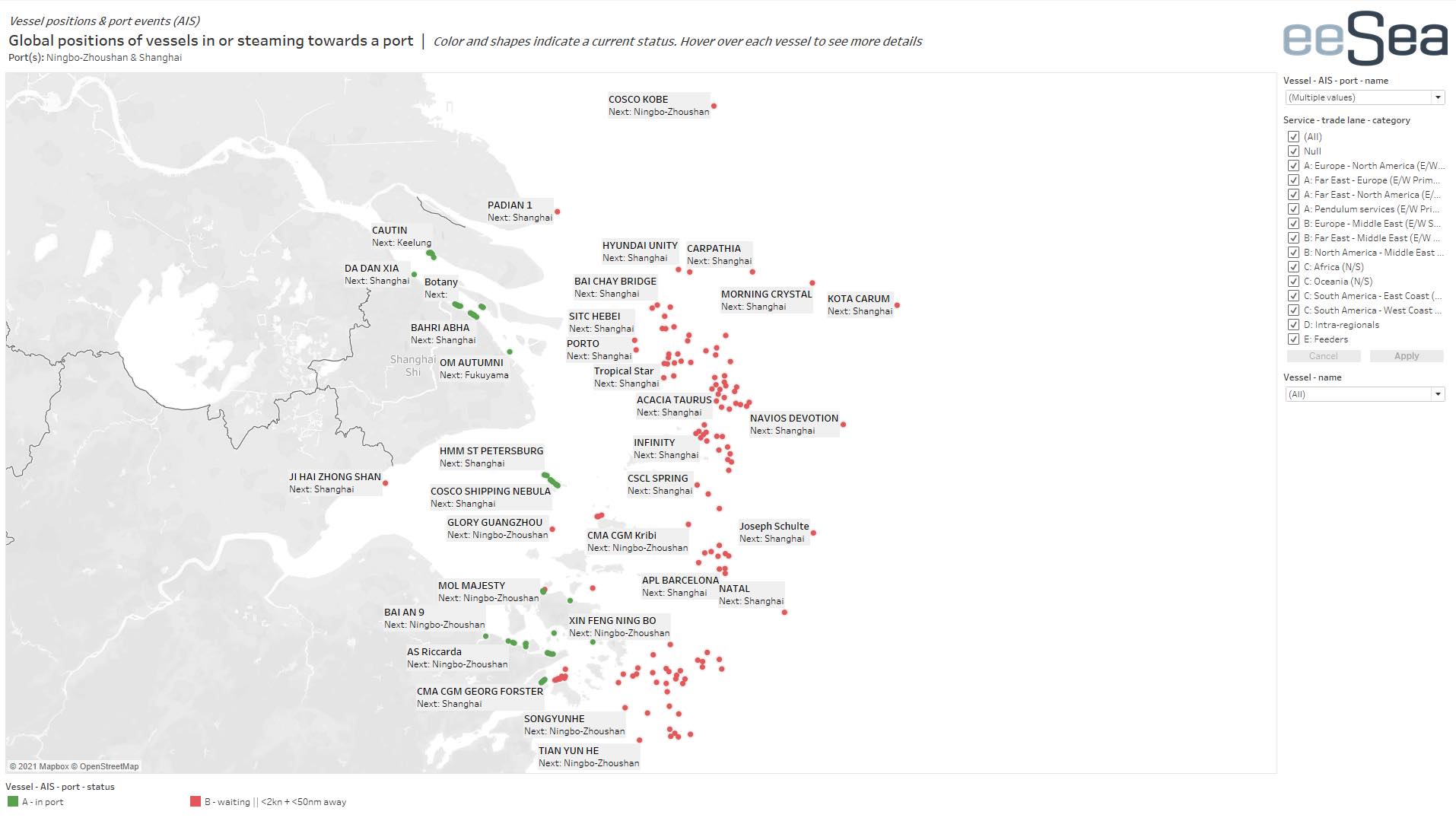
The huge volume of boxships at anchor at the two ports is carried in a map below created for Splash by Danish liner consultancy eeSea.
When a Covid-19 outbreak was detected at Yantian Port in late May, operations at the key southern Chinese export hub were slashed by 70% for most of June.
Since July 20, community-spread infections have been confirmed in roughly half of China’s provinces, sparking mass testing operations and localised lockdowns.
Newly reported positive Covid-19 cases in China have recently forced the country to re-introduce restrictions to curb the spread of the virus.
Most ports in the country are now requiring a nucleic acid test (NAT) for all crew, with vessels forced to remain at anchor until negative results are confirmed.
Many ports in the country are also requiring vessels to quarantine for 14-28 days if they previously berthed in India or performed a crew change within 14 days of arriving in China.
Lars Jensen, CEO of liner consultancy Vespucci Maritime, commented via LinkedIn last week, “Ever since the Yantian port partial close-down it has been clear that a risk for the container shipping sector would be the emergence of more Covid cases in other parts of China.”
On Monday, China reported 125 new Covid-19 cases, up from 96 a day earlier.
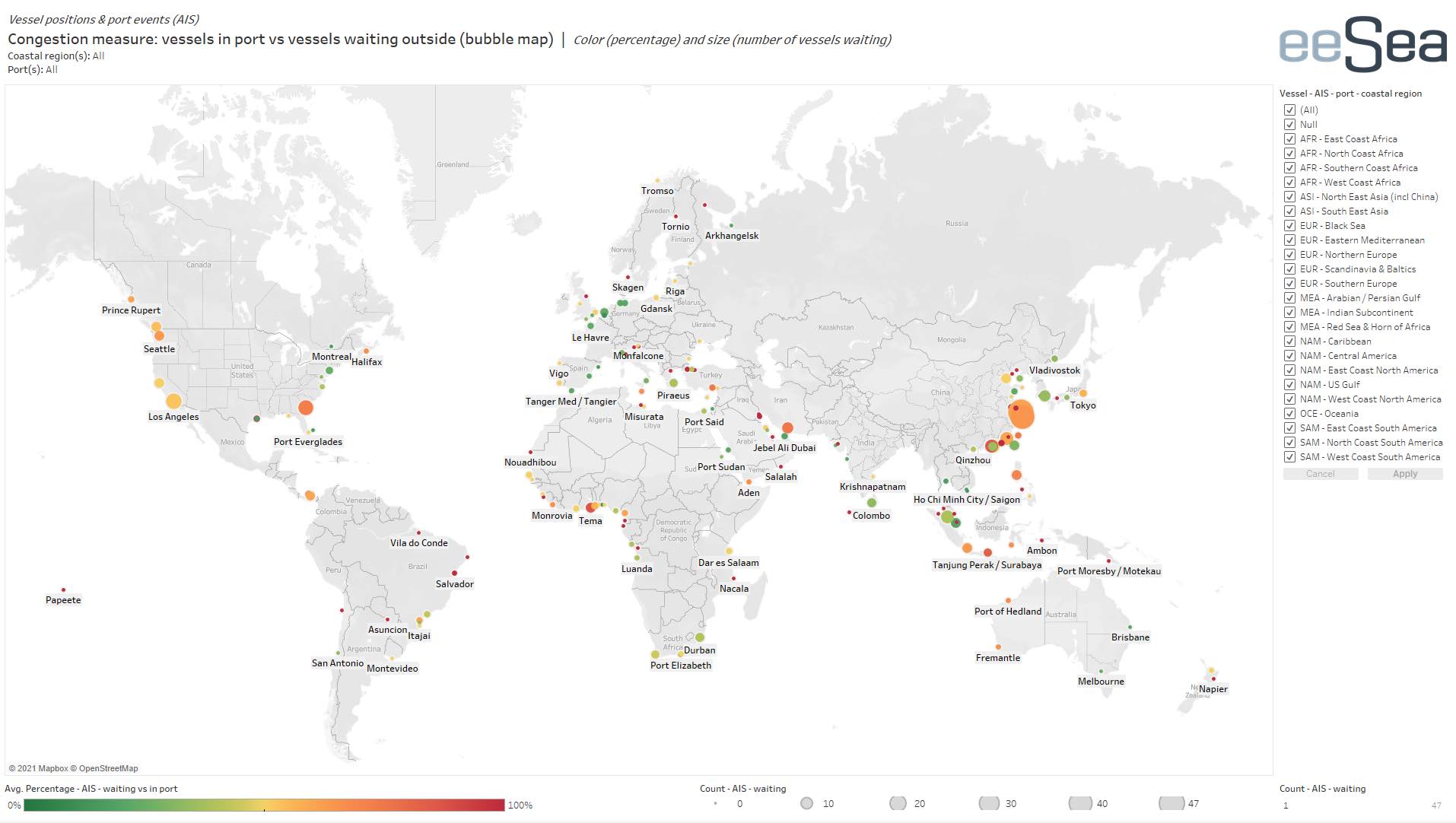
While Ningbo and Shanghai have the most amount of ships at anchor waiting for berth space, the global container port congestion looks increasingly worse as the below map compiled today by eeSea shows – the bubbles indicating ships backing up across five continents.
Source: splash247