A Classification of Dangerous Goods
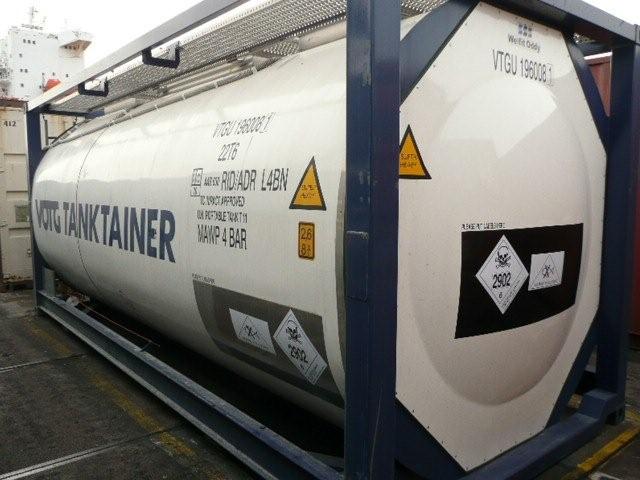
Transportation of dangerous goods through any route of transport requires a lot of precautionary and safety measures. Massive quantities of dangerous goods are transported each day through maritime transport modes. In order to enforce a proper method of transporting such hazardous materials (HazMat) there is a proper categorisation for them, which ensure utmost safety and precaution.
In terms of marine transport, the dangerous goods classification is based on SOLAS and MARPOL convention of the IMO which ultimately finds its place in the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code.
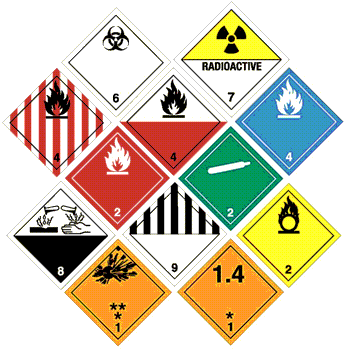
The types of dangerous goods, classified under nine groups can be listed down as follows:
- Group I: Explosive Materials
- Group II: Gaseous Materials
- Group III: Inflammable Liquids
- Group IV: Inflammable Solids
- Group V: Materials containing peroxides, easily oxidising contents
- Group VI: Substances highly toxic and infective
- Group VII: Radioactive substances and materials
- Group VIII: Erosive Materials
- Group IX: Dangerous materials and substances miscellaneous in nature
This list of classification is charted by the United Nations Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods.
Under all of these heads of categories, categories Group I to Group VI (except Group III) have various sub-heads denoted to further sub-divide the dangerous goods classification, so that a better ease in the packaging and storage of dangerous goods is enabled. The sub-categories of the types of dangerous goods can be enumerated as follows:
- Group I has six sub-classes ranging from explosives which have a major explosion threat to those which do not have that big a threat in terms of a mass-scale explosion respectively
- Group II has three sub-divisions for flammable gases, compressed gases and gases that cause health hazards due to their inhalation in that order
- Group IV has three sub-divisions for flammable solids, combustible materials and solids that have the tendency to give off inflammable gases when they come in tangency with water respectively
- Group V has two sub-classes categorising materials that easily oxidise and those which contain peroxides and have a tendency to cause harm when impacted, respectively
- Group VI also has two sub-divisions dealing with poisonous and radioactive materials and substances respectively
In the best interests of the shipping and business corporations that frequently carry out transportation of dangerous goods, a Dangerous Goods Safety Advisor (DGSA) has been appointed. The role and responsibility of the DGSA can be enumerated as follows:
– The DGSA has to ensure that the required rules and regulations pertaining to the packaging and storage of dangerous goods is met with as is the overall transportation aspect
– The DGSA looks after the investigation procedures from the company’s perspective in case of any accident or incident
– The advisor is also in-charge of the compilation of reports and data pertaining to the transportation of dangerous goods, required by the company management
The oceanic environment today is standing at a very vulnerable threshold. This is why the classification of dangerous goods for the oceanic transportation network becomes even more important and necessary. Through these measures the international bodies of authority can ensure that there are no chances of the marine eco-system degrading further. For, if the eco-system faces more problems, it will lead to a crisis not just for the creatures and plants but also for us humans who depend on the ocean for our livelihood.
References: businesslink, searates, cmu, hse